Jewish Languages -- European
By William Brinner
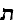




 _
_



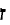




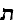




 _
_



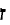




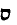 ''
''

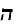 _
_
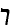

 Derekh ha-Shas and
Derekh ha-Shas and



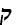




 Yiddishkeit.
Yiddishkeit.
Germanic has given rise to only one Jewish language -- Yiddish. This originated among the Zarphatic-speaking Jews of Ashkenaz -- they either moved eastward into German-speaking area or inhabited a Romance-speaking were taken over by a Germanic tribe. Here is what it looks like!
Nothing is known about the Jews of Germany between Roman times and Carolingian -- so
Jewish history there begins in 9th century CE. Old High German became the earliest
form of Yiddish, some remnants still known:




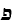 feter/
feter/


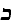


 onkel,
onkel,



 mume/
mume/



 mime/
mime/




 tante; as well as some elements of Zarphatic:
tante; as well as some elements of Zarphatic:




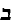

 davenen,
davenen,




 oren.
oren.
Ideas of Max Weinreich:
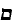


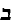
 _
_



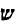 _
_
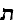

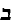
 _
_
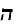
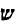

 "Ma'asseh avot siman l'vanim."
"Ma'asseh avot siman l'vanim."
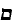




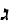 Gaonim rooted in
Gaonim rooted in




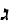 Gemara, Gemara and Written Law are one.
Gemara, Gemara and Written Law are one.
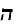


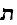
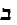 _
_

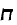


 _
_
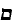

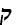

 _
_


 'eyn mukdam umeuhar batorah' (in Torah there is no earlier and later). Some strange
synchronisms: a new temporal relativity: time goes not only forward but backward.
Moses can meet Rabbi Akiva and both can meet Ba'al Shem Tov.
'eyn mukdam umeuhar batorah' (in Torah there is no earlier and later). Some strange
synchronisms: a new temporal relativity: time goes not only forward but backward.
Moses can meet Rabbi Akiva and both can meet Ba'al Shem Tov.
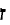

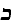

 _
_



 loshn ashkenaz, or
loshn ashkenaz, or






 "leshoyneynu", and it became a Jewish element. In 18th century, Rabbi Jacob Emden, in
contrasting Yiddish and German, says: "Yiddish is loshn ashkenaz, German is
"leshoyneynu", and it became a Jewish element. In 18th century, Rabbi Jacob Emden, in
contrasting Yiddish and German, says: "Yiddish is loshn ashkenaz, German is
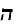
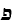
 _
_
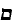



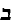
 _
_
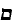
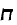
 _
_
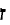

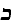

 _
_



 "lashon ashkenaz she-hem mevinim yafe." The Gentile language has become a Jewish language,
the Gentiles had only a historic-genetic relationship to it.
"lashon ashkenaz she-hem mevinim yafe." The Gentile language has become a Jewish language,
the Gentiles had only a historic-genetic relationship to it.
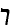


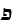

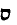




 shmeltsshprakh -- Fusion language. Here are some examples:
shmeltsshprakh -- Fusion language. Here are some examples:

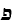
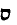 _
_
 _
_

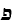


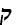

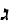 _
_




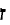 _
_


 _
_


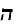 _
_





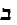 _
_

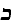







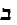 bentshn
-- benedicere (Old Italian);
bentshn
-- benedicere (Old Italian);

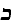



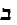 brokhe has
a different meaning than bentshn .
brokhe has
a different meaning than bentshn .




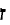 zeyde -- Slavic;
zeyde -- Slavic;




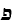
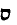



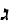 grosfater is
Western Yiddish, not Eastern.
grosfater is
Western Yiddish, not Eastern.

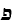
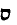 seyfer -- not
seyfer -- not
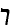


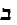 bukh or
bukh or



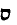 sidder , or
sidder , or

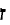
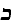
 makhzer ; each
has a different meaning.
makhzer ; each
has a different meaning.
Thus, the word
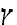


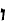
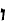
 shvarts
gives rise to compounds
shvarts
gives rise to compounds not found in German:

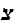


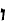
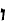



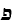 farshvartsn /
farshvartsn /


 -
-
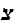


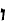
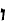
 shvarts-yor:
shvarts-yor:
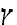


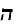 _
_
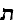

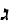 _
_
 _
_
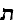

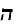
 _
_

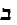
 _,
_,
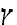


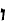
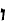
 _
_



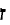 _
_


 _
_
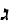


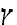


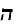 harts /
harts /
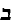


 leyv /
leyv /

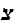


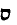 sertse --
same meaning, different sources:
sertse --
same meaning, different sources:


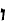
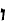 _
_


 _
_


 _
_
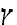


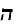 _
_
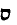



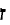
 mazl /
mazl /
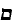


 shlim =
shlim =

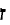



 shlimazl --
shlimazl --





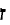


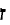

 dizmazaladu (known to Cervantes)
dizmazaladu (known to Cervantes)
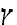

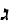


 sheygets,
sheygets,
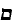

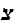


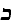
 shkotsim =
shkotsim =

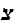

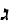


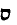

 _
_
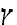


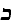
 shkots oysshegetsn
shkots oysshegetsn
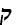


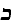

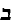 vokhedik,
vokhedik,
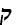

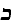


 milkhik,
milkhik,
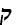





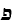 fleyshik.
fleyshik.




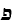 foter /
foter /





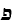 futer = father;
futer = father;




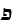 putter /
putter /




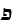 pitter = butter;
pitter = butter;



 neyn /
neyn /



 nayn = no;
nayn = no;



 nayn /
nayn /


 nahn = 9.
nahn = 9.





 _
_



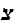 Tz'ena ur'ena (from the Song of Songs, 3:11), by Ya'akov ben Yitzhak
Ashkenazi, by end of 16th century CE. Oldest existing edition from 1622. Combination of
Tz'ena ur'ena (from the Song of Songs, 3:11), by Ya'akov ben Yitzhak
Ashkenazi, by end of 16th century CE. Oldest existing edition from 1622. Combination of



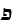 p'shat
p'shat



 d'rush
d'rush


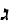


 _
_
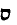



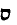




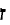

 La'az.
La'az.
Ladino -- La'az, originally a foreign gloss of Hebrew transliteration, based on
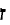


 _
_
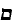
 " 'am lo'ez" in Psalms 114:1. Probably from
" 'am lo'ez" in Psalms 114:1. Probably from

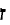 _
_
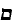
 _
_



 "Lleshon 'am zar".
"Lleshon 'am zar".
In Italy:






 latinar,
in Spain
latinar,
in Spain






 ladinar, (also in Provence), or
ladinar, (also in Provence), or


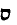




 romancar
in France
romancar
in France


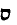





 aromancer.
aromancer.
Major classical work:


 _
_
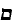

 "Me'am Lo'ez" -- 18th century CE. Started by Ya'akov Kulli,
d. 1730, completed by others. An ethico-homiletical work. For a long time, the only literature
of Sephardic families, reading considered a religious duty.
"Me'am Lo'ez" -- 18th century CE. Started by Ya'akov Kulli,
d. 1730, completed by others. An ethico-homiletical work. For a long time, the only literature
of Sephardic families, reading considered a religious duty.
A "Diaspora language", like Yiddish. In North, Amsterdam and London. Ladino is not
the spoken "Judeo-Spanish," Judezmo is. It is written, but so is Judezmo. It is the product
of the word for word translation of Hebrew texts -- Biblical and liturgical -- into a
Spanish that goes back to the 13th century. Earliest documents in Ladino from 1540.
A semi-sacred language transformed into a vernacular: Judezmo. The latter now very
francified because of Alliance (Israelite Universalle) schools. Termed Ladino by
Turkish Jews to cover their Jewish identity. Kol Yisra'el broadcasts in






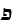
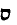

 -
-




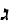 _
_


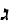


 Lingua Judio-Espanyol
It looks
like this.
Lingua Judio-Espanyol
It looks
like this.
Judezmo in Mediterranean area:
Zarphatic -- once of great importance, now essentially gone. Spoken in the Rhine-Moselle
area, mother tongue of French in Middle Ages, what is now called Old French. Jews of
Normandy spoke a Norman dialect; in Troyes, Champagnois; in Dijon, Burgundian.
Rabbinical decisions given in Old French, sometimes even language of prayer:
Hebrew Gallicized:


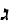
 agin =
agin =
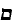


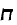 hayim;
hayim;
religious terms as well:


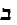





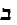 bonteable =
bonteable =


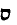
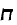 hasid;
hasid;




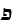 plain =
plain =



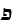 p'shat.
p'shat.
Jewish names --




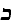 Colon =
Colon =
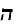


 Yonah;
Yonah;





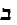 Bendit
Bendit
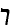



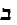 Barukh;
Barukh;
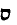

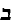

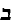 Vives =
Vives =
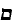


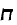 Hayim
Hayim





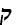 Quinet =
Quinet =
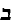
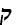

 Ya'akov (Jaquinet);
Ya'akov (Jaquinet);




 Monet =
Monet =




 Shim'on (Simonet)
Shim'on (Simonet)
From 12th century, la'az glosses appeared in French and English Jewry. 6 or more
glossaries of Bible from 13th century tens of thousands of old French words. Rashi alone
had 1300 glosses in Bible, 3500 in Talmud.
Shuadit -- this name for Judeo-Provencal first used in 1803 by
non-Jews in satires and comedies. Oldest texts are glosses in



 Ittur by Isaac
ben Abba Mari of Marseilles between 1170-1193. Other commentaries of
13th and 14th centuries give examples of Shuadit and Catalanit. Only
full text preserved are fragments of Esther, 14th century, and translation
of Siddur from the 14th or 15th century. Composed in vernacular for women.
Ittur by Isaac
ben Abba Mari of Marseilles between 1170-1193. Other commentaries of
13th and 14th centuries give examples of Shuadit and Catalanit. Only
full text preserved are fragments of Esther, 14th century, and translation
of Siddur from the 14th or 15th century. Composed in vernacular for women.
Hebrew-French declined in use after the Revolution. Called
ebraico vulgari .
One feature:t,s, tz all become f.
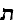

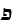 perat -->
perat -->
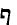

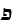 peraf ;
peraf ;
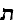

 emet -->
emet -->
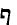

 emef ;
emef ;

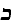
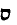 sekhel -->
(
sekhel -->
( )
)
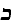
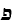 fekhe(l) ;
fekhe(l) ;
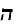


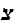 tzurah -->
tzurah -->
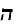


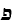 furah .
furah .
Also, y becomes sh (ch):
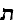



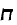

 yehudit -->
yehudit -->
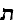




 shuadit ;
shuadit ;



 yayin -->
yayin -->



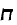 chayin ;
chayin ;

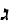

 yuge -->
yuge -->

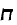

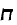 chuche .
chuche .
Italkian -- Italian Jews called





 Latino or
Latino or



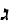


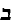 Volgare.
Dialect of the 13th century Rome, influenced by other central Italian provinces.
Became frozen after Jews were confined to the Ghetto in Rome from 1555 CE.
Volgare.
Dialect of the 13th century Rome, influenced by other central Italian provinces.
Became frozen after Jews were confined to the Ghetto in Rome from 1555 CE.
Earliest literature from 13th century, a lamentation for
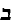

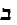 _
_


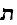 Tish b'Av.
Tish b'Av.
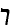


 'Arukh of
Natan ben Yehiel of Rome , form late 11th century, contains 600 Italian
words. Creation of words from Hebrew roots:
'Arukh of
Natan ben Yehiel of Rome , form late 11th century, contains 600 Italian
words. Creation of words from Hebrew roots:

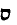



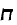
 achannoso From
achannoso From


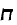 chen ;
chen ;





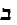

 dabberare from
dabberare from

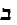
 dabber;
dabber;




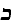
 achlone from
achlone from


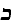
 akhlan;
akhlan;



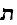 -
-


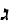


 _
_



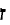

 -
-


 mal-mazzale mangia-tora
(one who reads with great speed);
mal-mazzale mangia-tora
(one who reads with great speed);




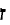 -
-




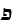 perdi-zeman = time-waster;
perdi-zeman = time-waster;



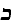



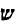 serichoddi from
serichoddi from
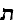

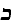


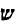 S'likhot;
S'likhot;

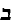

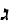


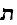 tongheva from
tongheva from

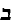


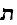 to'eva = crucifix ;
to'eva = crucifix ;





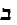 beridde from
beridde from
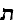


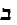 b'rit = penis ;
b'rit = penis ;





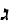
 ngarrele from
ngarrele from


 'arel = uncircumsized.
'arel = uncircumsized.
Yevanic -- a parchment MS of Yonah found in Crete, sale date 1263 CE, is
the earliest known document. Closer to ancient Greek than any relic of
early Byzantine literature. It is continued to be spoken and written in
Janina, Larissa, Chalcis, Corfu, Zante.
Under Nazis some Greek Jews used Yevanic to communicate. Today, except
for Ladino speakers, Greek Jews use standard Greek.
Tat -- Tats presumably descend from Iranian military colonies established during Sassanian period, 226-641 CE. Originally a Southwest Iranian dialect. Tati
influenced by NW Iranian and Turkish. Chiefly found in Makhachkala, Derbet, Kuba.
Before 1917 written in Hebrew characters, forced to Romanize in 1929, to
Cyrilize in 1939, One of the 9 official and literary languages of
Daghestan, in 1959 30,000 Jews listed as their mother tongue.

zebrin@socrates.berkeley.edu